Git integration (GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket)
Your Read the Docs account can be connected to your Git provider’s account. Connecting your account provides the following features:
- 🔑️ Easy login
Log in to Read the Docs with your GitHub, Bitbucket, or GitLab account.
- 🔁️ List your projects
Select a project to automatically import from all your Git repositories and organizations. See: Importing your documentation.
- ⚙️ Automatic configuration
Have your Git repository automatically configured with your Read the Docs webhook, which allows Read the Docs to build your docs on every change to your repository.
- 🚥️ Commit status
See your documentation build status as a commit status indicator on pull request builds.
Note
- Are you using GitHub Enterprise?
We offer customized enterprise plans for organizations. Please contact support@readthedocs.com.
- Other Git providers
We also generally support all Git providers through manual configuration.
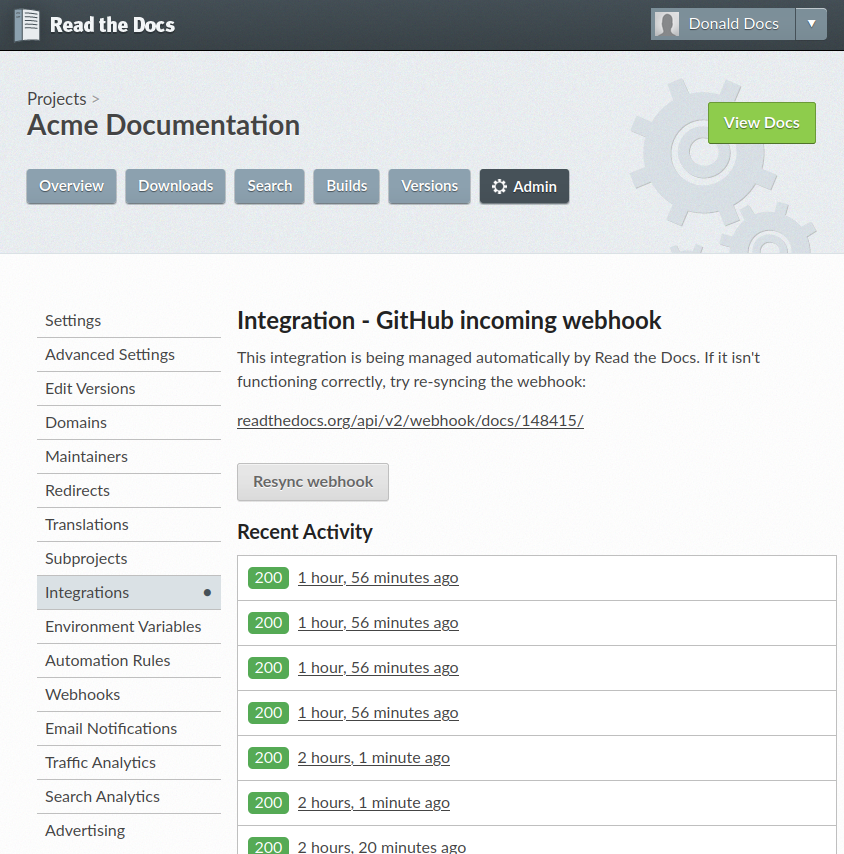
All calls to the incoming webhook are logged. Each call can trigger builds and version synchronization.
Read the Docs incoming webhook
Accounts with GitHub, Bitbucket, and GitLab integration automatically have Read the Docs’ incoming webhook configured on all Git repositories that are imported. Other setups can setup the webhook through manual configuration.
When an incoming webhook notification is received, we ensure that it matches an existing Read the Docs project. Once we have validated the webhook, we take an action based on the information inside of the webhook.
Possible webhook actions outcomes are:
Builds the latest commit.
Synchronizes your versions based on the latest tag and branch data in Git.
Runs your automation rules.
Auto-cancels any currently running builds of the same version.
Other features enabled by Git integration
We have additional documentation around features provided by our Git integrations:
See also
- Pull request previews
Your Read the Docs project will automatically be configured to send back build notifications, which can be viewed as commit statuses and on pull requests.
- Single Sign-on with GitHub, Bitbucket, or GitLab
Git integration makes it possible for us to synchronize your Git repository’s access rights from your Git provider. That way, the same access rights are effective on Read the Docs and you don’t have to configure access in two places.